Leda Home
Page

Introduction to the LEDA system (1990-1997)
LEDA is a prototype Legislative Design and Advisory System designed to
offer easy access to the Dutch Directives for Regulations (Aanwijzingen voor de
regelgeving)
These Directives consist of 346 directives regarding important drafting
issues and drafting activities. Aside from legislative technique issues, such
as terminology and model clauses, they also deal with structuring issues,
policy aspects, methodological issues, procedures, etc. Although they closely
resemble ordinary legal rules, they are of a different nature. They are not
always generally binding rules, but rather directives one can, in certain
cases, deviate from if strict application would lead to unacceptable
consequences.
The LEDA system provides legislative drafting assistance on the basis of
the Directives for Regulations in a methodical way, concurrent with the
information needs during the different drafting activities of the drafting
process. Furthermore, LEDA offers a form of knowledge-based IT support for some
specific drafting activities, e.g. LEDA makes it possible to check a draft bill
on conformity with some of the requirements of the Directives.
History and goals of the LEDA-project
Between 1991 and 1995 a prototype of the Legislative Design and Advisory
System LEDA was developed in the LEDA project which was carried out by
commission of the Netherlands Ministry of Justice. The LEDA project was aimed
at researching the possibilities and the actual development of a
practically-geared legislative IT drafting system which would assist the
professional legislative draughtsman of the Ministry on the basis of the
Directives for regulations. The main goal in developing the LEDA system was to make
the information of the Directives themselves easily accessible according to the
information-needs during the different stages of the drafting process. Since
the Directives were relatively new, at the time of the LEDA project,
informatized access to the Directives could provide quite a large advantage
over the relatively troublesome access to paper versions of the Directives.
A secondary goal of the LEDA project was to make the information referred
to by the Directives (secondary information) easily available to users of the
system. Many Directives, as it happens, do not prescribe what the solution to a
legislative problem must be, but rather what (kind of) activity should be
undertaken given a certain legislative problem. In many cases the Directives also
describe what kind of information must be used to perform a prescribed
activity.
A third goal of the LEDA project was to offer knowledge-based drafting
support for some specific drafting activities (such as checking a draft text
for conformity with the requirements as laid down in the Directives).
Developing LEDA
In order to develop LEDA, a well-known information-oriented system
development method (SDM) was adopted. During the development of the LEDA system
this method was used to gather the specifications for the LEDA prototype. The
environmental characteristics of the legislative drafting process were analysed
during the LEDA project in order to gather global specifications for the
systems. As a basis for this analysis the Directives for regulations were used.
By way of a detailed analysis of each separate Directive, in which each
Directive was \'atomised\' to the level of a single normalised drafting
activity, the structure of the legislative drafting process according to the
Directives was unveiled. During the LEDA project norm-frames were used for this
analysis. The analysed legislative drafting structure derived from the
Directives constitutes a legislative design-step-model which can be used to
develop a system.
The functionalities of the LEDA system
LEDA is a prototype Legislative Design and Advisory System designed to
offer easy access to the Dutch Directives for Regulations (and secondary
information) in a methodical way, concurrent with the information needs during
the different drafting activities of the drafting process. Furthermore, LEDA
offers a form of knowledge-based IT support for some specific drafting
activities, e.g. LEDA makes it possible to check a draft bill on conformity
with some of the requirements of the Directives. LEDA contains three major
functionalities: methodological support, document drafting and document
assembly support, and knowledge-based information retrieval. The LEDA
functionalities are integrated throughout the system. The LEDA system is
equipped with a representation of the design step model, which gives users
methodological support by offering design modules and design levels, and easy
access to relevant information through the functionalities of these modules and
levels. To be able to work comfortably with the system, LEDA\'s functionalities
have been integrated in a well-known word-processing system.
The combined functionalities make LEDA an integrated authoring-system, i.e.
an IT system which assists users in solving legislative problems on the basis
of legislative information and, furthermore, supports its users in authoring a
legislative document, based on the solved legislative problems, which meets
with the requirements of the Directives.
Technically, the LEDA system is a hypertext network which allows different
kinds of navigation and working patterns within the system. Users can navigate
freely through the system\'s network. The information which the system contains
is hypertextually linked in various ways.
AI and language technology in LEDA
LEDA is equipped with a knowledge-based mechanism which allows users to
check parts of their draft texts on conformity with Directives requirements. A
so-called conceptual dependency parser checks draft texts for Directives
concepts. These Directives concepts are represented in LEDA by way of leaflets
which contain different associated Directives and key words or key phrases. By
comparing the Directives concepts with concepts in the text of a draft, LEDA
can determine the relevance of certain Directives for the draft text.
Click for more specific information on LEDA
Some screendumps
from the 1996/1997 version of WordLeda
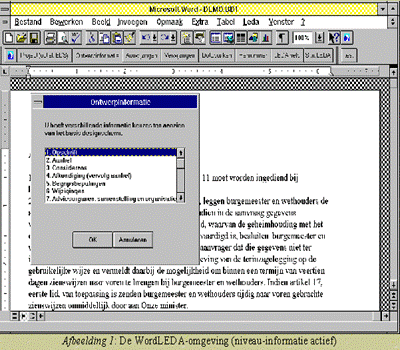
fig 1.
Levelstructure
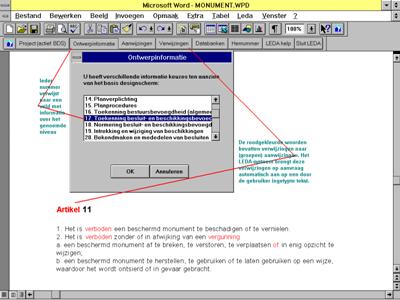
fig. 2 LEDA
parsing text and making references
Articles and publications on
LEDA 1990-1997
 w.j.m.voermans@law.leidenuniv.nl
w.j.m.voermans@law.leidenuniv.nl